Cybersecurity: Protecting Our Digital Frontiers in an Ever-Changing Landscape
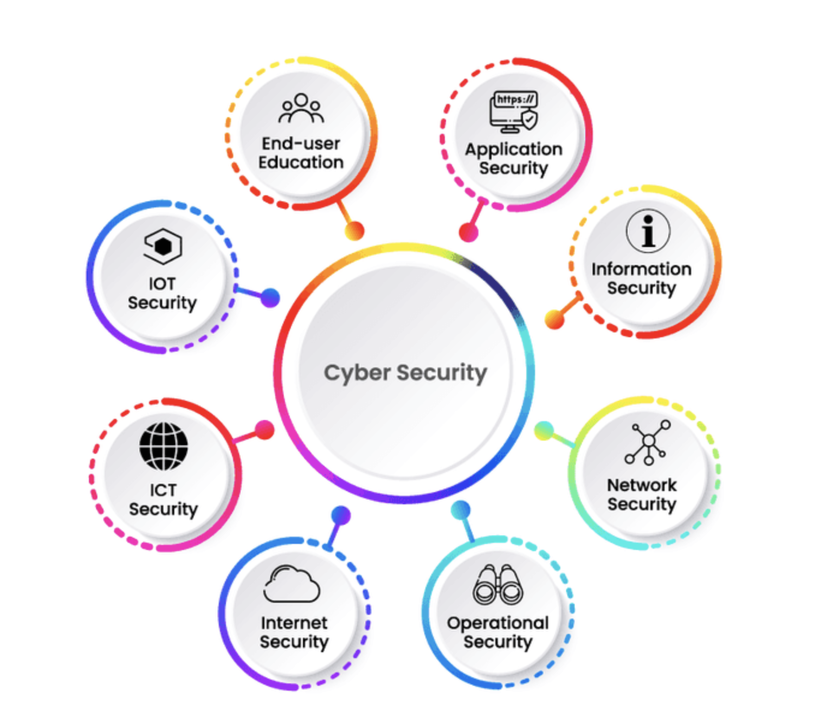
Introduction
In our increasingly interconnected world, the digital realm has become an integral part of our daily lives. We rely on technology for communication, work, shopping, and entertainment. However, this convenience comes with a growing concern: cybersecurity. In this comprehensive article, we will delve into the multifaceted world of cybersecurity, exploring its importance, the evolving threat landscape, strategies for protection, and the future of digital defense.
The Evolving Threat Landscape
The rapid expansion of digital technology has given rise to a diverse array of cyber threats, ranging from simple phishing schemes to sophisticated nation-state attacks. Understanding the complexity of the threat landscape is the first step toward effective cybersecurity.
1. Malware: The Silent Invader
Malware, short for malicious software, is a broad category encompassing various forms of harmful code designed to infiltrate and compromise computer systems. It includes viruses, worms, Trojans, ransomware, and spyware. Malware can be distributed through deceptive emails, infected websites, or compromised software downloads.
2. Phishing: The Art of Deception
Phishing attacks involve duping individuals into revealing sensitive information such as usernames, passwords, or financial data. Cybercriminals impersonate trusted entities—banks, businesses, or government agencies—through deceptive emails, messages, or websites. Falling prey to phishing can result in identity theft, financial loss, and compromised personal information.
3. Data Breaches: A Breach of Trust
Data breaches involve unauthorized access to an organization’s or individual’s sensitive information. These breaches can occur due to vulnerabilities in security systems, human error, or targeted attacks. Stolen data may include personal records, credit card numbers, trade secrets, or intellectual property, posing severe privacy and financial risks.
4. Ransomware: The Digital Extortionist
Ransomware attacks have surged in recent years. Cybercriminals use ransomware to encrypt an individual’s or organization’s data and then demand a ransom for its release. Paying the ransom is discouraged, as it funds criminal activities and provides no guarantee of data recovery.
5. Insider Threats: Trusted but Dangerous
Insider threats involve individuals within an organisation misusing their access privileges to compromise security. These threats can be malicious, with employees intentionally harming their employers, or inadvertent, with well-intentioned employees falling victim to scams or phishing attacks. Detecting and mitigating insider threats require a delicate balance between trust and vigilance.
The Importance of Cybersecurity
In a world where digital technology permeates every aspect of our lives, cybersecurity has emerged as a fundamental necessity. Here are some key reasons why cybersecurity is of paramount importance:
1. Protection of Personal Information
Our lives are increasingly documented online, making strong cybersecurity measures essential for safeguarding sensitive personal information. This includes Social Security numbers, medical records, financial details, and even personal conversations. Without adequate protection, this information can fall into the wrong hands, leading to identity theft, fraud, and severe privacy breaches.
2. Preservation of Business Continuity
For organisations, cybersecurity is not merely about data protection but also about ensuring business continuity. Cyberattacks can disrupt operations, damage reputation, and result in significant financial losses. Robust cybersecurity practices are vital to maintain the stability and integrity of an organisation’s systems and operations.
3. National Security
Cybersecurity isn’t limited to individuals and businesses; it’s also a matter of national security. State-sponsored cyberattacks and cyber espionage can have far-reaching consequences, affecting critical infrastructure, government operations, military defence, and the overall economy. Protecting against these threats is a top priority for governments worldwide.
4. Trust in Digital Transactions
As we increasingly rely on digital transactions for banking, shopping, communication, and more, trust in these transactions is paramount. Effective cybersecurity ensures the integrity and confidentiality of these transactions, fostering confidence in the digital ecosystem.
5. Protection of Intellectual Property
Intellectual property, including trade secrets, proprietary software, and innovative research, is a valuable asset for many organizations. Cybersecurity safeguards this intellectual property from theft or espionage, preserving a company’s competitive advantage and innovation.
Cybersecurity Best Practices
Now that we’ve established the importance of cybersecurity, let’s explore some best practices for individuals and organisations to bolster their digital defences:
1. Regular Software Updates
Keep your operating system, software applications, and antivirus programs up to date. Developers release patches to address known vulnerabilities, and failing to update can leave your system exposed to attacks.
2. Strong Passwords and Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Utilise complex, unique passwords for each online account, combining letters, numbers, and special characters. Whenever possible, enable MFA, which adds an extra layer of security by requiring multiple forms of verification.
3. Email Vigilance
Exercise caution with emails. Avoid clicking on links or downloading attachments from suspicious or unknown sources. Verify the legitimacy of requests for sensitive information, even if they appear to come from trusted entities.
4. Employee Training
Organisations should provide comprehensive cybersecurity training to their employees. This education should cover topics like recognizing phishing attempts, social engineering techniques, and best practices for data protection.
5. Regular Backups
Regularly backup important data to secure locations, both offline and in the cloud. In the event of a ransomware attack or data breach, backups can be a lifeline, ensuring that critical information remains intact.
6. Network Security
Implement robust network security measures, including firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and access controls. Regularly review network logs for signs of unusual activity that may indicate a security breach.
7. Incident Response Plan
Develop a well-documented incident response plan outlining the steps to take in the event of a cyber incident. This plan can minimize damage, facilitate a swift recovery, and ensure that all team members know their roles in managing and mitigating the incident.



