Between The Worlds: A Device For The Deafblind Community With Synthesized Voice
Deafblindness, a singular sensory disability that encompasses both vision and hearing impairments, presents an array of distinctive challenges and obstacles for those grappling with its profound impact. The intertwining of these two sensory impairments can significantly impede communication, access to information, mobility, and engagement in daily activities, thereby necessitating a deeper understanding of the nuanced struggles faced by people with health conditions.
An innovative startup from India has introduced the idea of creating a device for the deafblind community that will enable them to communicate using modern speech synthesis and voice recognition systems.
Chief among the challenges faced by the deafblind community are the formidable barriers that hinder seamless communication. Given the reliance on tactile sign language, finger spelling, and Braille, effective communication often requires intricate physical proximity and deliberate touch-based interactions, a process that demands substantial time, patience, and spatial coordination, thereby adding layers of complexity to everyday conversations. Additionally, the absence of universally standard communication methods can impede effortless interaction, underscoring the need for tailored strategies that cater to the diverse communication needs of the deaf-blind people.
The startup founders aim to provide deaf-blind individuals with a means of communication without relying on sign language. All developments were carried out with assistance and support from the Indian Institute of Technology Bombay (IIT Bombay).
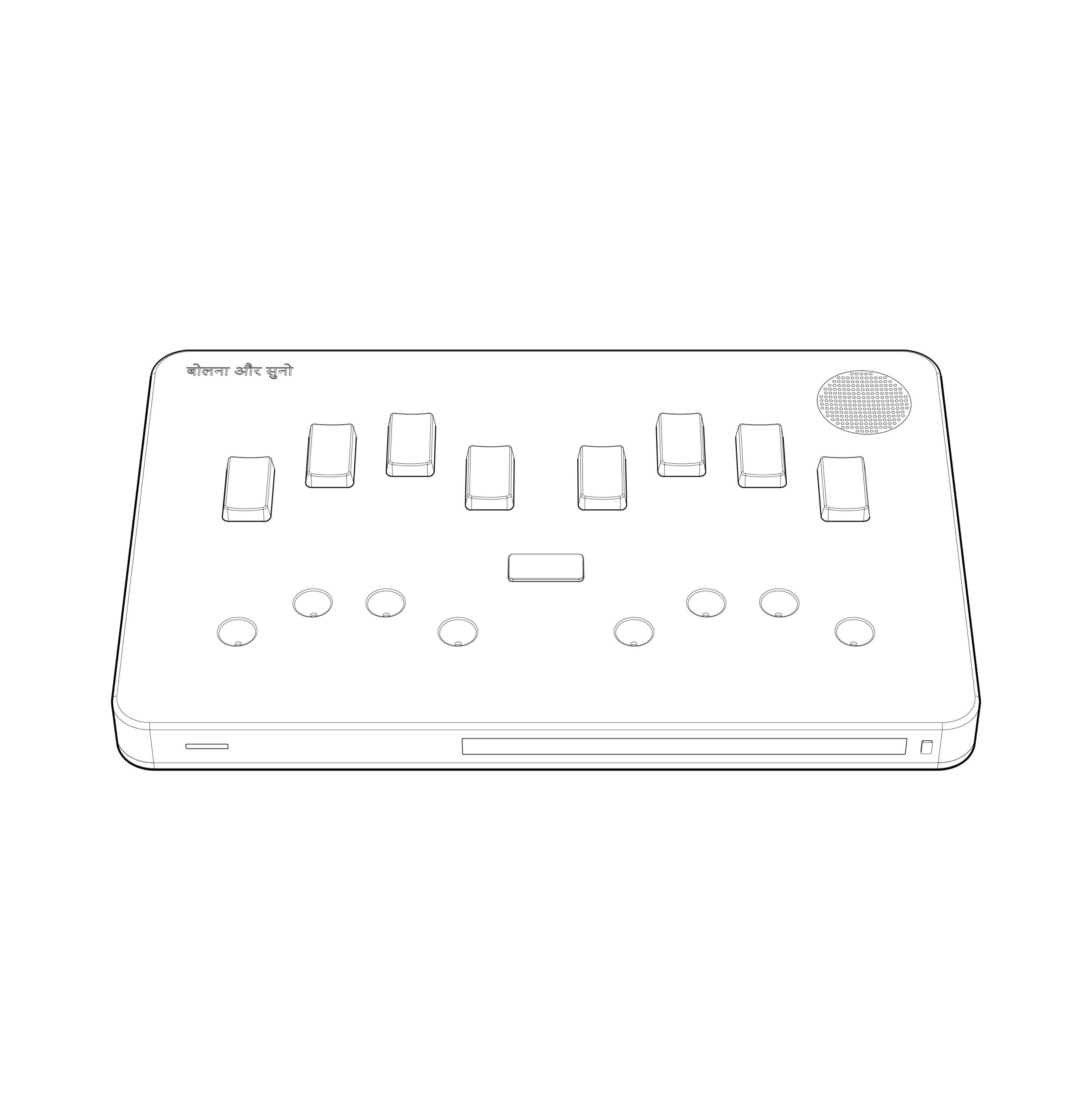
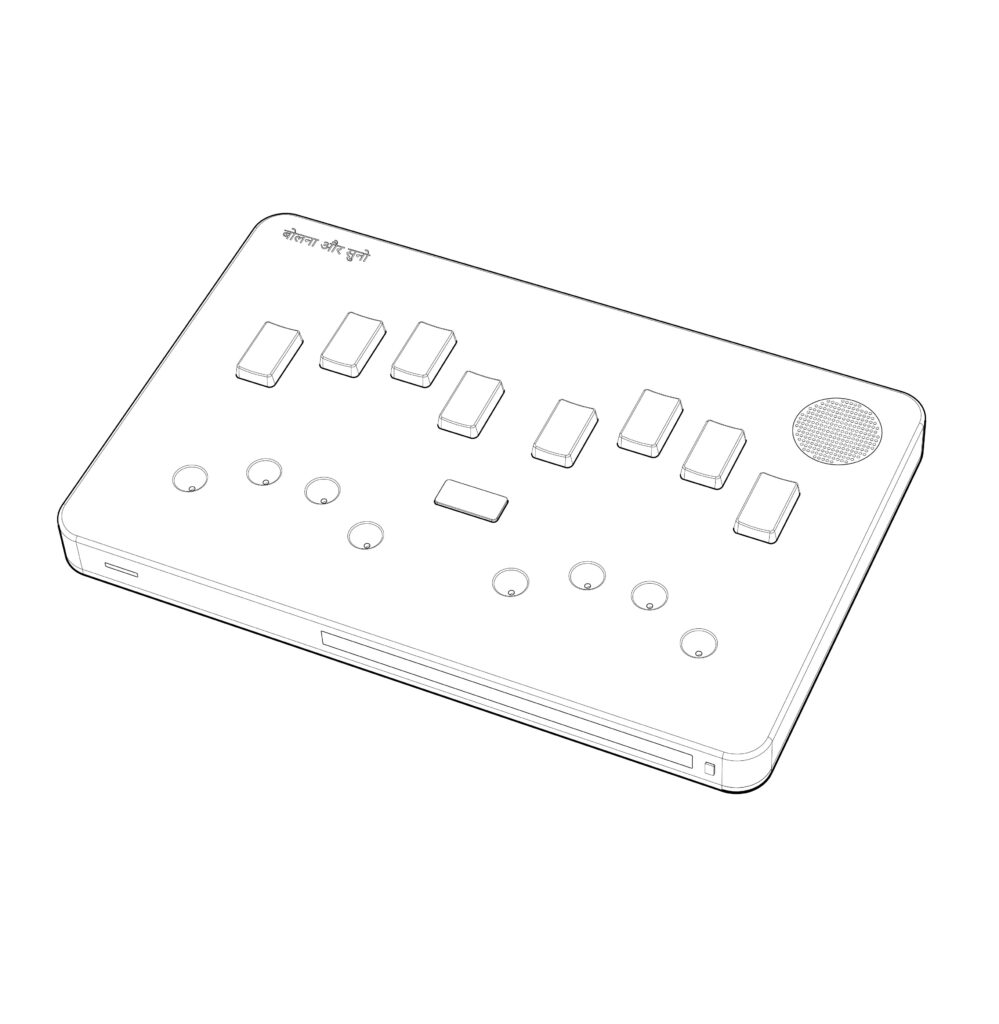
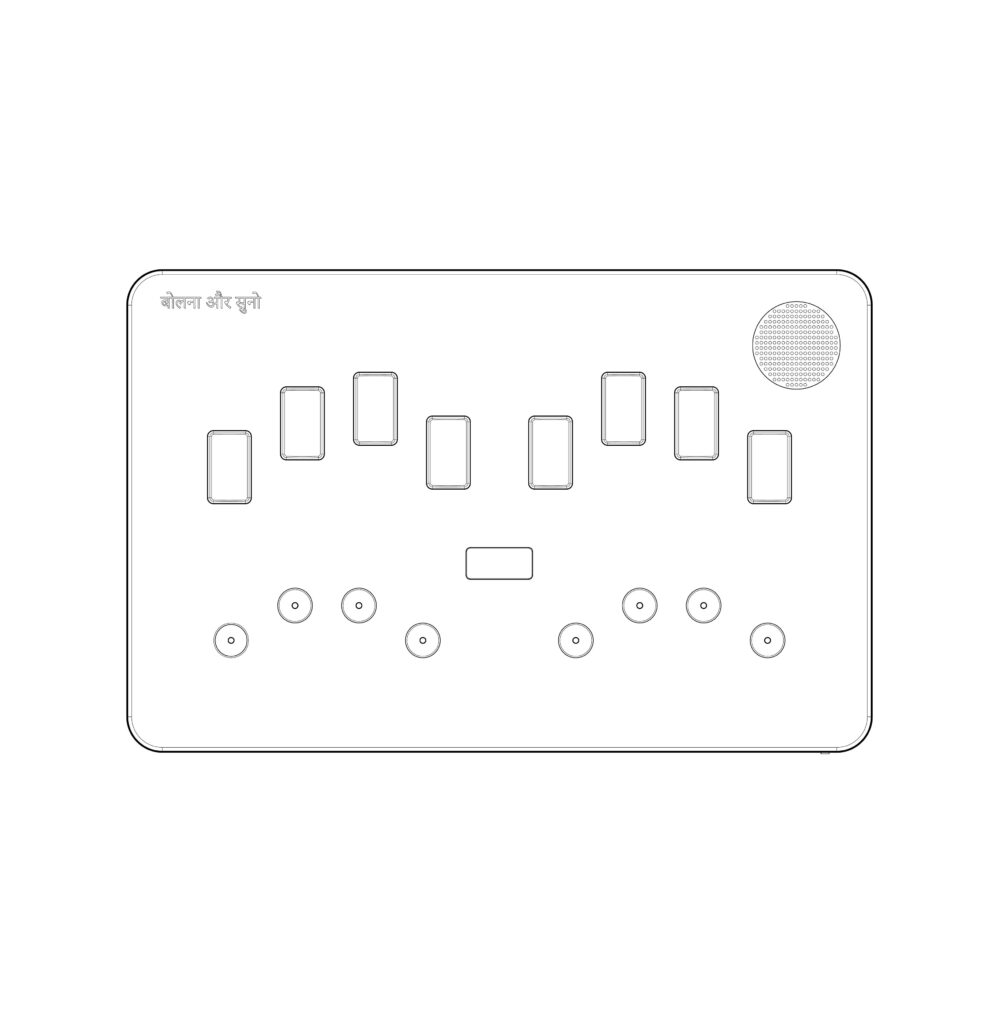
The communication method involves using a standard keyboard found on Braille displays. One of the most striking features of this device is vocalization of typed text by a synthesized voice. Currently, the device allows communication only in English, but the startup promises to add other languages by 2017.
The principle of word recognition for the people with dual sensory loss involves the user placing their fingers on special cavities where text, spoken by their interlocutor, is sequentially outputted. The text is conveyed by exerting influence on all 4 fingers of each hand alternately, according to a specific letter in Braille font. In this system, characters are represented by patterns of raised dots that can be felt with the fingertips. Small tactile elements are located in the cavities, allowing individuals unfamiliar with the Braille font to use the device for reading, as there is no need to recognize Braille dots because they turn into single touches in the device.
This tactile method empowers users to decipher and interpret the conveyed information with precision and clarity. By incorporating this unique approach to word recognition, the device not only facilitates seamless communication between individuals, but also enhances accessibility for those with specific communication needs. Furthermore, this method fosters a dynamic and engaging form of interaction, bridging the gap for individuals who may have limitations.

Access to information, educational resources, and employment opportunities proves to be another formidable hurdle for the people with multi-sensory impairment. Traditional printed material, visual media, and auditory content can pose insurmountable barriers, thereby curbing the ability of deaf-blind individuals to independently pursue educational and professional avenues. The absence of widespread availability of accessible formats and technologies further exacerbates these hurdles, thus underscoring the pressing need for comprehensive and universally accessible resources.
A speech synthesis device provides access to educational materials, books, articles, and other resources, expanding learning and self-development possibilities and contributing to better integration into the educational processes and daily life. A speech synthesis device is an invaluable tool for people with health conditions. Technologies that are capable of combining various sensory capabilities represent an essential step toward creating a more accessible, inclusive, and supportive society.
Emotional well-being and social integration cannot be understated. Deaf-blind individuals often encounter feelings of isolation, marginalization, and a sense of disconnection from the broader community due to the unique challenges they face in social interactions and communication. This underscores the critical need for fostering inclusive environments that acknowledge and account for the varied emotional and social needs of people with health conditions. A speech synthesis device is an invaluable tool for people with health conditions or impairments.
Looking ahead, the startup harbors aspirations of forging collaborative partnerships, with a keen eye on potential collaborations with Orbit Research, a distinguished company in India that currently markets its products in the United States.
This innovative amalgamation of technology, inclusivity, and support stands as a testament to the indomitable spirit driving towards a more accessible and inclusive society, where the convergence of diverse sensory capabilities finds expression in transformative technological ventures crafted for the betterment of all.
In conclusion, the multifaceted challenges faced by the deafblind community demand a holistic, collaborative, and inclusive approach that prioritizes tailored communication strategies, accessible educational resources, mobility aid innovation, and the cultivation of empathetic and accommodating social landscapes. By fostering greater awareness, advocating for comprehensive support mechanisms, and embracing technological advancements, we can collectively pave the way for a more inclusive and supportive environment that respects the unique needs and triumphs of people with health conditions.



